There are three types of additives commonly used in polycarbonate. One is the antioxidant, which can be divided into hindered phenolic main antioxidant and phosphite ester coantioxidant because of its different protection principle. The second type is the material processing and forming lubricants, commonly used is stearic acid lubricants; The third type is to adjust the color of the powder, commonly used is organic pigments. This paper mainly studies the effect of these three auxiliaries on the color of polycarbonate after hot processing.
Note:
(1) Antioxidant 168: tri (2, 4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphite;
(2) Lubricant PETS: pentaerythritol stearate;
(3)Antioxidant 1076: β – (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate n-octadecyl alcohol ester.
Effect of antioxidant additives on yellowing of polycarbonate
1.Effect of phosphite antioxidants on yellowing of polycarbonate
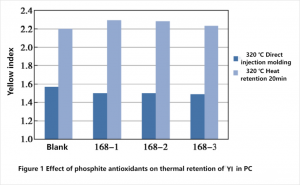
The color change of polycarbonate from different manufacturers 168 and blank polycarbonate before and after heat retention in the injection molding machine is shown in Figure 1.
As can be seen from Figure 1, the yellow index (YI) value of the direct injection samples decreased to a certain extent after the addition of 168 from different manufacturers, indicating that 168 has a protective effect on the color of the material during processing. After 20 minutes of thermal retention, the yellow index of polycarbonate was higher than that of blank polycarbonate after the addition of phosphite antioxidant, which may be due to the fact that phosphite antioxidant was gradually consumed and changed into pentavalent phosphorus in the process of high temperature, and the antioxidant ability was lost. On the other hand, small molecules and impurities in antioxidant further affected the decomposition of polycarbonate at high temperature. The YI value of the polycarbonate was higher than that of the blank sample after 20 minutes of thermal retention at 320℃.
2.Influence of hindered phenolic antioxidants on yellowing of polycarbonate
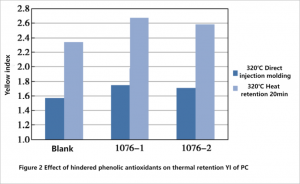
The color change of polycarbonate from different manufacturers 1076 and blank polycarbonate before and after heat retention in the injection molding machine is shown in Figure 2.
It can be seen from the blue bar chart in Figure 2 that the YI value of polycarbonate samples injected directly with 1076 from different manufacturers is higher than that of blank polycarbonate, and the yellow index of the material does not decrease as much as 168. As can be seen from the bar chart, after 20 minutes of thermal retention, the YI value of 1076 added is higher than that of blank polycarbonate, and the range is increased compared with that before thermal retention, indicating that the main antioxidant, as a long-acting antioxidant, does not effectively protect the high-temperature processing process like phosphite antioxidant. Moreover, due to the influence of the structure of hindered phenol, the YI value of 1076 added is higher than that of blank polycarbonate. Although the phenol oxygen free radical generated after the loss of hydrogen of hindered phenols is relatively stable, it may produce quinone chromophore group at high temperature, leading to the increase of YI and affecting the optical properties of polycarbonate.
Effect of stearic acid lubricants on yellowing of polycarbonate
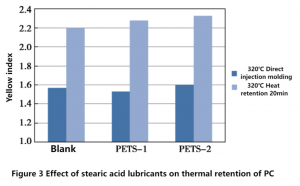
The color change of polycarbonate with PETS from different manufacturers and blank polycarbonate before and after heat retention in the injection molding machine is shown in Figure 3.
As can be seen from the comparison of the blue bar chart in Figure 3, there is no significant difference in YI value between blank polycarbonate and polycarbonate with lubricant added after direct injection. After thermal retention, YI value increased slightly, but the effect was limited, possibly because there was a very small amount of pentaerythritol or stearic acid residue in the lubricant, which would lead to alcoholysis and transesterification of polycarbonate at high temperatures for a long time, accelerating the aging of polycarbonate and resulting in increased yellowing.
Effect of color powder on yellowing of polycarbonate
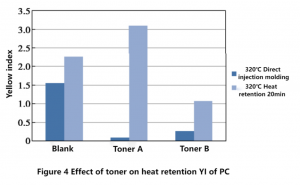
The color changes of polycarbonate with different kinds of color powder and blank polycarbonate before and after thermal retention in the injection molding machine are shown in Figure 4.
It can be seen from Figure 4 that the YI value of polycarbonate can be significantly reduced by the addition of two kinds of toner at the same amount. However, after 20 minutes of thermal retention at 320℃, the color difference of toner A has a large rebound, while the change range of toner B is similar to that of blank particles, indicating that the application effect of different kinds of toner under short-term high-temperature processing and long-term high-temperature retention has a large difference. May cause severe discoloration of polycarbonate by high temperature processing。
Analysis of heat resistance of toner
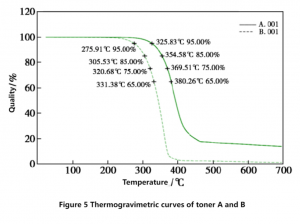
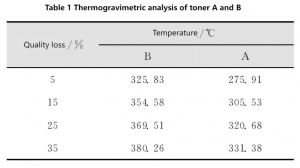
TGA detection was carried out on toner A and toner B respectively, and the heating rate rose to 700℃ at 10℃/ min under nitrogen atmosphere. The difference in heat resistance between the two is shown in Figure 5. The temperature corresponding to the four points of 5%, 15%, 25% and 35% weight loss of the two toners in Figure 5 are shown in Table 1.
It can be seen from the curve in Figure 5 that the thermal stability of the two toners is significantly different. The initial thermal decomposition temperature of toner B is about 325℃, while the initial decomposition temperature of toner A is only 275℃, and toner B is about 50℃ higher than toner A during weight loss.
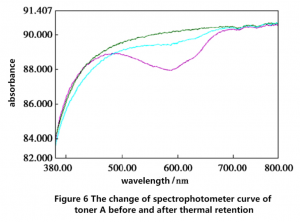
At the wavelength of 600nm, the sample of polycarbonate with color powder A added before and after thermal retention and the blank polycarbonate were compared and analyzed by spectrophotometric curves, and the results were shown in Figure 6. The three curves in the figure are the blank polycarbonate curve from top to bottom, the polycarbonate thermal retention curve after adding toner A, and the polycarbonate thermal retention curve before adding toner A.
As can be seen from Figure 6, the absorption peak of toner A was obvious at 450~700nm, and the absorption peak was significantly weakened after 20 minutes of thermal retention, indicating that the hair base group of some toner A had changed, resulting in serious discoloration of polycarbonate.
Yellowing analysis of polycarbonate additive
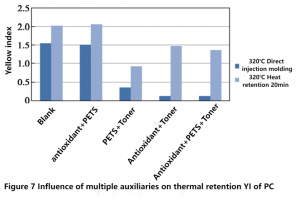
168, PETS and toner B were used for further analysis, and the heat retention injection molding experiment was carried out with polycarbonate after the antioxidant, lubricant and toner were mixed in two or three, and the results were shown in Figure 7.
As can be seen from the first two bar charts in Figure 7, YI values of polycarbonate added with antioxidants and PETS are basically the same as those of blank polycarbonate, with no significant difference, and the two have little effect on yellow of the material during high-temperature processing, which is consistent with the results of adding the two additives alone.
The color difference before and after the addition of color powder and PETS was not much different from the blank color difference, indicating that PETS and color powder did not interact with each other, and had little effect on the yellowing of polycarbonate.
As can be seen from the last two bar charts in Figure 7, after the combination of antioxidant and toner and the combination of the three, the polycarbonate showed yellow increase, indicating that the antioxidant and toner interact with each other. The possible reason is that the antioxidant itself or its high-temperature decomposition products react with the toner, affecting the chromophore group of the toner.
Summary
1. Direct injection molding after adding phosphite antioxidants to polycarbonate can protect the appearance of polycarbonate and reduce the YI value of the product, but long-term hot processing will lose the protective effect; YI values of polycarbonate were higher than those of blank polycarbonate after injection and thermal retention for 20 minutes after the addition of hindered phenolic antioxidants.
2. There was no significant difference in YI value between the polycarbonate of PETS and the blank polycarbonate before and after thermal retention, indicating that PETS themselves would not significantly affect the optical properties of polycarbonate.
3. The thermal stability of toner is more important, and the toner with poor heat resistance may change color after a long time of hot processing, thus affecting the appearance of the material itself, and the antioxidant and toner will cause partial failure of the toner under a long time high temperature environment, affecting the color of polycarbonate.
SYNTHOLUTION TECH is a global supplier of additives for the modification of plastics and coatings, including UV absorbers, antioxidants, light stabilizers and flame retardants, which have been widely used by customers in Europe, the United States and the Asia-Pacific region.
Enquiries are welcome at any time: little@syntholution.com
Post time: Aug-21-2023